M-3258 (M3258, M 3258)
$250.00 – $1,500.00
M-3258 (CAS No.: 2285330-15-4), orally bioavailable, potent, reversible and highly selective immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 (β5i) inhibitor. M3258 exerts high biochemical (IC50=3.6 nM) and cellular (IC50=3.4 nM) potency against the LMP7 subunit.
Synonyms: M3258, M 3258, M-3258, immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 (β5i) inhibitor
For Research Use Only.
- Product Details
- Description
- Additional information
- More Offers
Description
APIM050047: M3258 (M-3258, M 3258) is an orally bioavailable, potent, reversible and highly selective immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 (β5i) inhibitor.
CAS No.: 2285330-15-4
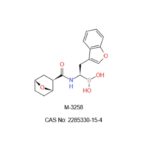
IUPAC/Chemical Name: ((S)-2-(benzofuran-3-yl)-1-((1R,2R,4S)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxamido)ethyl)boronic acid
Molecular Formula: C17H20BNO5
Molecular Weight: 329.2
Purity: >99% by Achiral and Chiral HPLCs
QC: Achiral and Chiral HPLCs, MS, NMR, and Quantitative Elemental Analysis Report
Solubility: Soluble in DMSO
Storage: Store at 0 °C (short term), -20 °C (long term), Desiccated
Note: Please contact us for COA, Spectra, and SDS information.
Background Information:
Proteasomes are large multicatalytic complexes that are central components of the cellular machinery for maintenance of protein homeostasis. The barrel-shaped 20S core particle of proteasomes consists of 28 subunits assembled in four rings of seven subunits each. The core particle of the broadly expressed constitutive proteasome (cP) contains the distinct proteolytic subunits β1 (PSMB6), β2 (PSMB7), and β5 (PSMB5), which possess caspase-like, trypsin-like, and chymotrypsin-like proteolytic activity, respectively. The differential substrate preferences of each subunit enable the processing of diverse ubiquitinated proteins in cells. A distinct core proteasome particle called the immunoproteasome (iP) contains the unique proteolytic subunits β1i (LMP2 and PSMB9), β2i (MECL1 and PSMB10), and β5i (LMP7 and PSMB8) with chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like, and chymotrypsin-like activity, respectively. The iP is predominantly expressed in cells of hematolymphoid origin4−7 and can be induced in other cell types by exposure to inflammatory stimuli such as IFNγ or TNFα.
Aside from its essential function in the maintenance of protein homeostasis, the iP also degrades pathogenic proteins and generates peptidic fragments, which are more efficiently loaded on the class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC I) for antigen presentation compared to cP-derived peptides. Furthermore, the iP-specific proteolytic subunits, in particular LMP7, play an essential role in restoring homeostasis in cells under elevated proteotoxic or oxidative stress. The essentiality of proteasomes for the viability of multiple myeloma (MM) cells has been underpinned by the approval
and wide application of the proteasome inhibitors bortezomib, carfilzomib, and ixazomib. These drugs interfere with the activity of multiple cP and iP proteolytic subunits.10 While this nonselective mechanism delivers robust clinical efficacy in MM, it is also associated with diverse toxicities including thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and cardiotoxicity, which can lead to dose reductions, less frequent regimens, or cessation of treatment and thus limit the therapeutic potential of these drugs. The restricted expression and unique functional features of iP-specific subunits have led to considerable interest in the potential of selective iP inhibitors in diverse disease settings.3,12,15 Recent reports have suggested that therapeutic efficacy in preclinical models of inflammation and autoimmunity requires dual inhibition of the iP subunits LMP2 and LMP7.15−18 However, in the case of preclinical cancer models, the therapeutic effects of inhibition of individual iP proteolytic subunits or multiple subunits remain less well characterized, with most preclinical reports to date only describing the activity of dual LMP2/7 inhibitors or compounds with only partial selectivity against the cP subunit β5.[1]
LMP7 inhibitor M3258 (M-3258) (CAS No 2285330-15-4) is an orally bioavailable, potent, selective, reversible inhibitor of the large multifunctional peptidase 7 (LMP7, β5i, PSMB8) proteolytic subunit of the immunoproteasome; a crucial component of the cellular protein degradation machinery, which is highly expressed in malignant hematopoietic cells including multiple myeloma. M3258 was previously shown to deliver strong in vivo preclinical efficacy in multiple myeloma xenograft models, as well as a more benign non-clinical safety profile compared to approved pan-proteasome inhibitors, exemplified by a lack of effects on the central and peripheral nervous systems and cardiac and respiratory organs. Here we describe preclinical PK/PD and PK/efficacy modelling which led to a prediction of the PK profile, and the efficacious and safe dose ranges of M3258 in human which were used to guide the design of the phase I dose-escalation trial of M-3258 in >3 line relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) patients.[3]
Mouse, rat, dog and monkey PK, plasma protein binding and intrinsic clearance data were used to estimate a half-life of approximately 6 hours for M3258 in human. The human total clearance and volume of distribution for M3258 were predicted to be 0.033 L/h/kg and 0.28 L/kg, respectively, whilst oral bioavailability was estimated to be above 80%. LMP7 proteolytic activity was assessed as a PD readout in human multiple myeloma tumor cells xenografted to mice as well as in dog peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). A strong PK/PD relationship was observed for M3258 across both species. LMP7 inhibition by M3258 also correlated strongly with anti-tumor efficacy in multiple myeloma xenografts, with maximal efficacy observed at M3258 exposure delivering sustained inhibition of tumor LMP7 activity. Quantitative PK/PD/efficacy modeling predicted the biologically efficacious dose (BED) of M3258 upon oral application to be between 10 – 90 mg daily in human. By incorporating data from nonclinical safety studies, these data suggest an attractive human PK profile of M3258, enabling oral application, as well as an improved human therapeutic index compared to approved pan-proteasome inhibitors. M3258 is being investigated in a phase I, first-in-man, 2-part, open label clinical study designed to determine the safety, tolerability, PK, PD and early signs of efficacy of M3258 as a single agent (dose-escalation) and co-administered with dexamethasone (dose-expansion) in participants with RRMM whose disease has progressed following > 3 prior lines of therapy and for whom no effective standard therapy exists. Integration of these data will guide the selection of the BED for potential further clinical development of M-3258.[3]
Synthetically, M-3258 (CAS No 2285330-15-4) and its analogues were synthesized in eight steps from commercially available aliphatic, benzylic, or bicyclic methylene bromide.[1]
Target: LMP7
IC50: 3.6 nM (Biochemical), 3.4 nM (Cellular)
In Vitro: M-3258 (M3258) inhibits human LMP7 with a mean IC50 of 4.1 nM. M3258 displays weak activity against the constitutive proteasome subunit β5 (mean IC50=2519 nM). M3258 potently inhibits LMP7 in the human multiple myeloma cell lines MM.1S and U266B1 and in human, rat, and dog PBMCs with IC50s between 2 and 37 nM.[2]
M3258 induces a >four fold accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins with an EC50 of 1980 nM in MM.1S cells. M3258 interferes with immunoproteasome function. M3258 also induces apoptosis assessed by caspase 3/7 activity (EC50=420 nM;>3.5-fold induction) and reduces MM.1S cell viability (IC50=367 nM).[2]
In Vivo: M-3258 (M3258) (1 mg/kg; 10 mg/kg) shows superior antitumor efficacy in selected multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma xenograft models compared with the approved nonselective proteasome inhibitors bortezomib and ixazomib.[2]
What is the solubility of M-3258 in vitro?
250 mg/mL in DMSO (Need ultrasonic)
What is the solubility of M-3258 in vivo?
1. Solvent: DMSO, PEG300, Tween-80, and saline
Please add 10% DMSO, 40% PEG300, 5% Tween-80, and 45% saline in order; solubility ≥ 2.08mg/mL.
2. DMSO and 20% SBE-β-CD in salin
Please add 10% DMSO and 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in saline) in order; solubility 2.08 mg/mL (need ultrasonic).
3. DMSO and corn oil
Please add 0% DMSO and 90% corn oil in order, solubility ≥ 2.08 mg/mL.
Reference:
[1]. Klein, M. et al. “Structure-Based Optimization and Discovery of M3258, a Specific Inhibitor of the Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (β5i)”, J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10230-10245.
[2]. Sanderson, M. P. et al. “M3258 Is a Selective Inhibitor of the Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (β5i) Delivering Efficacy in Multiple Myeloma Models”, Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.
[3]. Lignet, F. et al. “Quantitative PK/PD Prediction of the Efficacious and Safe Dose Ranges of the LMP7 Inhibitor M3258 for Phase I Application in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients”, Blood 2019, 134, 5582.
[4]. Sloot, W. et al. “Improved nonclinical safety profile of a novel, highly selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 (M3258)”, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 429, 115695.
Frequent questions related to “M3258 (M-3258) (CAS No 2285330-15-4), a Reversible and Highly Selective Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (β5i) Inhibitor”:
Does M-3258 bind mouse LMP7?
Does M-3258 bind mouse Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7?
Who makes M-3258?
What is M-3258?
What is the mechanism of action for M-3258?
Popular searches related to “M3258 (M-3258) (CAS No 2285330-15-4), a Reversible and Highly Selective Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (β5i) Inhibitor”:
M-3258 results
M-3258 fda approval
M-3258 mechanism of action
M-3258 price
M-3258 side effects
M-3258 LMP7 Inhibitor
M-3258 synthesis
M-3258 analogue
M-3258 structure activity study
M-3258 in vitro
M-3258 in vivo
M-3258 supplier
M-3258 clinical study
M-3258 LMP7
M-3258 β5i
M-3258 Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7
M-3258 Cytotoxicity
M-3258 Target
M-3258 Inhibitor
LMP7 Inhibitor
LMP7
Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7
Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (β5i)
Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP7 (β5i) Inhibitor
Additional information
| Size | 10 mg, 100 mg, 5 mg, 50 mg |
|---|